Introduction
Immune-based therapies, including the anti-CD38 antibody daratumumab (Dara), and most recently bispecific antibodies (BsAb) targeting CD3 and BCMA, GPRC5D or FCRH5 are increasingly important strategies used to treat Multiple Myeloma. However, there are concerns that the prolonged use of these therapies predisposes patients (pts) to increased rates of infection, partly due to hypogammaglobulinaemia. To this date, most clinical trials on Dara and BsAb do not consistently capture rates of hypogammaglobulinaemia and leaves the use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) as prophylaxis to individual investigator discretion. There are currently a paucity of studies documenting IVIg as a means to reduce infection risk in these pts.
Patient and Methods
All patients with MM who started Dara or BsAb therapy at St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne from Jan 2021 to Dec 2022 were included in this retrospective chart review. Patients who received more than 2 months of treatment were included. The evaluation period for each patient began at the time of first Dara or BsAb dose and ended at the cut-off date of 28 th June 2023. The two time periods were “ON IVIg” defined as any time within 30 days of last IVIg administration and “OFF IVIg” defined as any time >30 days from last IVIg administration. The primary outcome was the incidence rate of all grade infections (expressed in events/person-year) during periods of ON IVIg vs OFF IVIg. Secondary outcomes included incidence rate of severe infection (CTCAE Grade 3-5). Incidence rate ratios (IRR) and the corresponding 95% confidence intervals were calculated using the Exact Poisson method.
Results
A total of 52 Dara or BsAb treated pts were identified of which 7 were excluded due to treatment cessation from progressive disease within 2 months. The remaining 45 pts were included in the study of which 16 were on Dara, 16 on a BCMA BsAb and 13 on a non-BCMA BsAb. All 16 of the patients on Dara received Dara as a triplet combination. Median age was 65 (IQR 59-70), 25 (56%) were male and median prior lines of therapy received was 1 (IQR 1-3). At the start of treatment, 34 pts (76%) had documented hypogammaglobinaemia of which 12 (27%) had severe hypogammaglobinaemia (defined uninvolved IgG <4.0 g/L). Median functional IgG was 5.0 g/L (IQR 3.9-6.5). Eleven pts (24%) were already on IVIG prior to Dara or BsAb therapy and a further 18 (40%) were commenced on IVIG during the course of treatment.
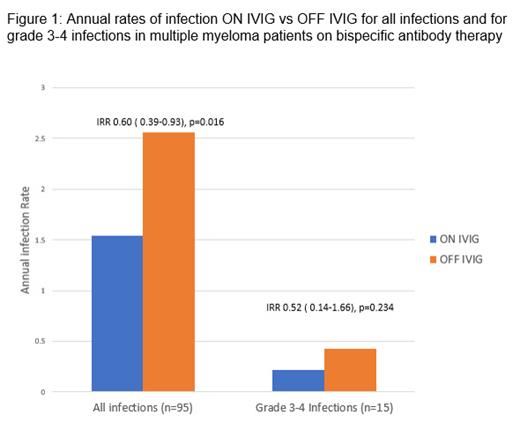
At the cut-off date, 30 (67%) pts were still receiving Dara or BsAb therapy. Median time on treatment was of 8.94 months (IQR 5.06-14.30). The proportion of time ON IVIg for the cohort was 53%. Patient receiving BsAb spent a greater proportion of time ON IVG than patients receiving Dara-based therapy (56% vs 42%, p <0.002). There were 95 all grade infections during the evaluated period, most commonly in the respiratory tract; upper respiratory tract infections (36%), lower respiratory tract infections (31%) and COVID-19 (12%). There were 15 documented severe infections of which 10 occurred during the OFF IVIG period. There were no infection related deaths. The median time to first infection from commencement of Dara or BsAb was 3.12 (IQR 1.25-5.61) months. The rate of all grade infections ON IVIG was 1.54 (95% CI 1.07-2.15) per person years and lower compared to 2.56 (1.95-3.29) per person years OFF IVIG with IRR of 0.60 (95% CI 0.39-0.93; p=0.016) (figure 1). Rate of severe infections was 0.22 (0.07-0.51) and 0.43 (0.20-0.78) per person years respectively with IRR of 0.52 (0.14-1.66; p=0.234). BsAb therapy had a higher all grade infection rate vs Dara-based therapy; 2.86 (2.23-3.62) vs 1.39 (0.91-2.03) per person years respectively; IRR 2.06 (1.30-3.38; p=0.001)
Conclusion
There are high rates of pre-existing hypogammaglobinaemia in MM patients even during early lines of treatment. The use of IVIG during immune-based therapies appears to significantly reduce the yearly rate of all grade infections by 40% in our cohort. Differences between the rates of severe infection ON IVIg and OFF IVIg are not significant due to small number of events. Further prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings, towards an evidence-based approach in IVIg support for patients with myeloma on novel immunotherapies.
Disclosures
Quach:Sanofi: Consultancy, Other: receipt of study materials; GSK: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: receipt of study materials; Leadership or fiduciary role, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Leadership or fiduciary role; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: receipt of study materials, Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal